Trimble 4700/5700/R7 - How to execute a post-processing kinematic (PPK) survey from start to finish
Trimble 4700/5700/R7 - How to execute a post-processed kinematic (PPK) survey from start to finish
About post-processed kinematic surveying
Post-processed kinematic (PPK) surveys are generally used for mapping or for surveying points where only several cm of precision are needed, such as 1) mapping out a feature such as a falt scarp or a shoreline; 2) recording the locations of sample sites; or 3) measuring the positions of markers such as stakes on a glacier to determince ice velocities. Occupation times for survey points are on the order of seconds. Data must be post-processed to achieve high-precision results; this requires a processing program such as Trimble Geomatics Office.
PPK surveys require data from at least two receivers: a ’base’ (reference) receiver and a ’rover’ (moving) receiver. You may use as many rover receivers as you wish. If you have access to raw data from a reference station already operating at an appropriate sample rate in your area (within 10 km of your survey), there is no need to set up an additional base station; note that the logging rate at the base, however, must be at least as high as the desired survey rate.
There are two types of survey methods in PPK surveys: topo points and continuous surveys. Topo points are short (usually 15 second) occupations, e.g. over a sample site or survey marker. Continuous survey mode allows ongoing data collection at a specified logging interval, e.g. every 5 seconds; continuous mode is used for mapping.
Planning the Survey
Geography. The base station should be located within 10 km of the area to be surveyed: the closer, the better. No line-of-sight (visibility) is required between the base and the rover(s).
Base. The base GPS antenna can be set up over an existing mark or a newly established mark, or, if no repeat surveying will be needed, placed directly on the ground. Correspondingly, the antenna mount used (if any) will depend on project needs. For a repeatable survey, you will need a way to center and level the antenna over your mark. If you are establishing a base marker for the first time, plan to collect at least an hour’s worth of data. See the UNAVCO Knowledgebase for more information on antenna mounts (/questions/394/).
Coordinate system. Applying a specific coordinate system during data collection of a PPK survey is not recommended, as you can apply coordinate systems during data processing. Note that if you are referencing a previous survey, you must use the same projection and datum that was used before. Record the projection and datum used for future surveys. If you are starting from scratch, consider using the universal transverse mercator (UTM) coordinate system; determine your zone by checking e.g. http://www.dmap.co.uk/utmworld.htm.
Data logging. Choose a logging interval before starting the survey. The base receiver must have a logging interval at least as high as the rover receiver’s; data from the rover can only be processed if corresponding data are collected at the base. The logging interval will depend on the survey goals. If mapping, think about how often you need a data point. For example, if doing a detailed survey or surveing from a vehicle, a 1 Hz (1 second) logging interval may be appropriate. For less detailed work and/or if walking, a 5 second logging interval may be appropriate.
Things to know before and during the survey:
Base GPS antenna type: _____________ (usually Zephyr Geodetic)
Rover GPS antenna type: _____________ (usually Zephyr or Zephyr Geodetic)
Base GPS antenna height measurement method: _____________ (usually "Bottom (or Top) of notch" or "Bottom of antenna mount")
Rover GPS antenna height measurement method: _____________ (usally "Bottom of antenna mount")
The survey controller
A survey controller is recommended for running the rover receiver. The survey controller gives control over the survey and records metadata that facilitates data organization. Note that the TSC1 survey controller will not work with the R7 receiver.
The menu system is very similar for the Trimble TSC1, TSCe, and TSC2. There may be some slight variations in wording from what is shown here, depending on which controller you are using, but the general flow should be the same.
Navigation is also similar between controllers, although the TSC1 has no stylis or touch-screen and the TSCe and TSC2 do. Drop-down menus are indicated by a right-pointing arrow inside a circle. To see a drop-down menu in the TSC1, highlight the menu item and push the right arrow on the controller; in the TSCe and TSC2, touch the arrow. To go back a screen, press the "Esc" key (TSC1) or option (TSCe, TSC2). To get to the main menu, press the "Menu" key or option.
Each survey controller is powered by a removable battery; however, when plugged into a receiver the controller will run off the receiver’s power.
Preparation
Survey Controller
To save time in the field, configure your survey in the survey controller beforehand.
Create a Job
-
Turn on the survey controller by pushing the green power button.
If needed, enter the "Survey Controller" program by double-clicking the corresponding icon.
The main menu consists of 6 options on the screen. Select "Files" in the top left.
In the TSC1, select "Job management," then "New" (F1 key). In the TSCe, select "New Job".
Give the job a name using the letter and number keys and hit "Enter". In the TSC1, select a memory location for the job; suggested setting is Main memory. Hit OK (F1).
Select "Coordinate system" (in the TSCe and TSC2, double-click on it or highlight it and press the enter (arrow) key); suggested setting is "No projection/no datum". Reference frames are best utilized in data processing rather than data collection.
Select coordinate system settings. For "No projection/no datum," suggested settings are Coordinates: Ground, Reference elevation: [elevation within 100 meters of your base elevation], Use geoid model: No. Hit OK.
Set the Survey Style
From the main menu, select "Configuration" in the top right.
Select "Survey Styles"-->"PP Kinematic" or "PPK" -->"Rover options".
Survey type: PP Kinematic
Logging device: [Choose Controller or Receiver; suggested setting is Controller]
Auto file names: [Choose Yes or No; suggested setting is Yes]
Logging interval: [Choose logging interval, e.g. 5 seconds; depends on survey goals--this will be your logging interval both for continuous and for point surveying]
Elevation mask: [Enter elevation mask; suggested setting is 13 00’00"; this is the elevation angle from the horizon below which no data will be collected from satellites]
PDOP mask: [Enter PDOP mask; suggested setting is 6.0 but should be set higher in difficult surveying conditions (limited sky view); this is a quantitative expression of satellite geometry, with lower numbers representing more favorable geometries]
Antenna height: [Enter antenna height if known--can be modified in the processing or in the field]
Type: [Select antenna type from list]
Meas. to: [Select antenna height measurement method]
Serial number: [Enter antenna serial number, if known]
Hit Enter or Accept when done to get back to the PP Kinematic menu.
Select "Base options".
Survey type: PP Kinematic
Logging device: [Receiver]
Logging interval: [Select logging interal; must be at least as frequent as rover, e.g. 5 seconds]
Elevation mask: [Enter elevation mask; suggested setting is 13 00’00"]
Antenna height: [Enter antenna height--can be modified later]
Type: [Select antenna type from list]
Meas. to: [Select antenna height measurement method]
Part number: [Enter antenna part number, if not already filled in]
Serial number: [Enter antenna serial number, if known]
Hit Enter or Accept when done to get back to the PP Kinematic menu.
Select "Topo point"
Auto point step size: [Enter auto point step size; suggested setting is 1; this automatically names points measured with the last character being a number 1 higher than that of the previous point measured]
Quality control: [Select quality control option; suggested setting is QC1]
Auto store point: [Select Yes or No; suggested setting is Yes; this automatically stores a point after the minimum conditions specified below are met]
Occupation time: [Enter minimum occupation time; suggested setting is 0m 15s; this specifies how long (minimum) you would like to occupy a survey point]
Number of measurements: [Enter minimum number of measurements; suggested setting is 3; this specifies how many measurements you would like to collect before the controller stores your survey point (an occupation time of 15 s and number of measurements of 3 will specify the same requirements at a logging interval of 5 seconds, but will be different at a logging interval of 1 second; the survey controller will always go by the most robust setting, e.g. will measure for 15 seconds (minimum occupation time) rather than 3 seconds (minimum number of measurements) for a logging interval of 1 second)]
Hit Enter or Accept when done to get back to the PP Kinematic menu.
Press the Menu key to get back to the main menu. You are done configuring your survey.
Equipment
If you are using a 5700 or R7 receiver, make sure there is a compact flash card in the receiver and enough memory for your survey (base station).
Make sure there is enough memory on your survey controller for your survey. If using a TSC1, make sure there is a compact flash or PCMCIA card in the controller.
Charge batteries. If using internal batteries, charge them in the receiver by plugging the receiver into an AC outlet using the AC power cable.
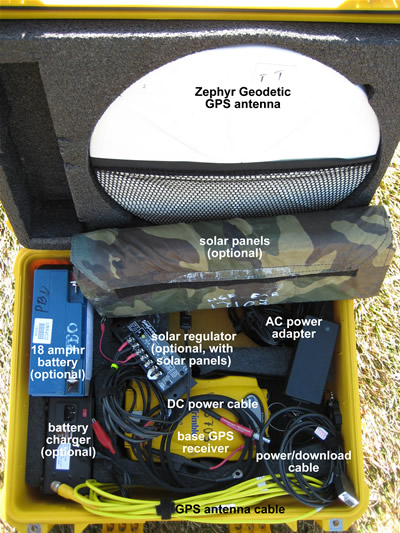


UNAVCO NSF EAR base GPS unit: typical packing (left) and view of all components (right).
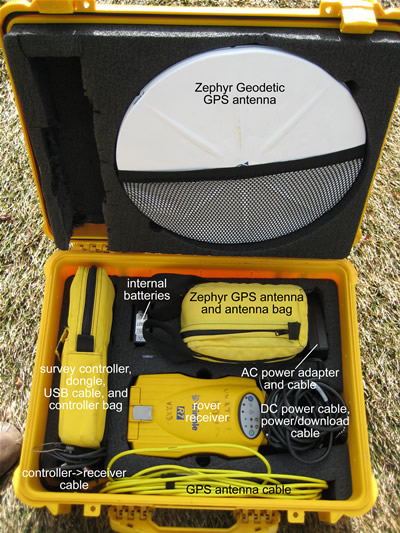
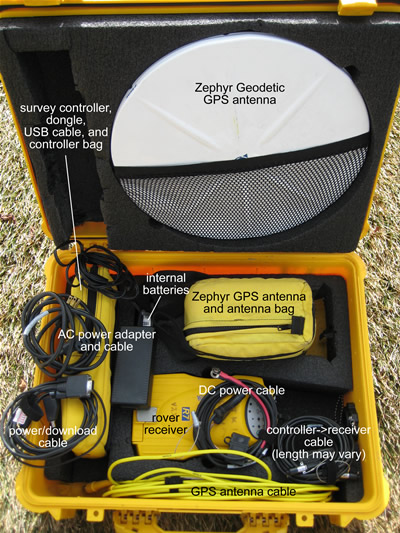


UNAVCO NSF EAR rover GPS unit: typical packing (left) and view of all components (right).
In the Field
Setting up and starting the base station
Base station setup may vary depending on the project goals. The suggested setup includes a high-precision (stable, centered, and level) and repeatable antenna setup. Antenna setup instructions will depend on the mount used. The base station should have good sky view; it must track at least 5 satellites in common with the rover at all times.
The base must be collecting data at all times when the rover is running in order to be able to process the rover data; set up the base station before starting the rover.
Set up the GPS antenna.
Level antenna mount where needed. Make sure the mount is centered over the mark.
Attach antenna to mount.
Align the antenna to true north where needed.
Measure and record the antenna height and the antenna height measurement method.
Attach the antenna cable to the antenna, if you haven’t already. Use the 90 degree connector for the antenna; pass the straight connector through the pass-through in the equipment case. DO NOT kink the cables; they are expensive, important, and subject to damage.
Connect the receiver to the battery (if using an external battery) using the battery cable and/or to an AC outlet using the AC power cable and port(s) 2 or 3 of the receiver. To connect the cable, align the red dot on the connector with the red dot on the receiver and push straight in. NEVER TWIST the connector, as the pins inside may break. The receiver will power up automatically if attached to external power.
If you are using a receiver with the UNAVCO default configuration, your survey will start automatically when you connect the receiver to power. The sample rate is 15s. If this sample rate is sufficient for you, there is no need to use the survey controller to configure the base receiver. Observe the lights on the receiver panel: a slow blink on the satellite light indicates the receiver is tracking 4 or more satellites; any light (’amber’) on the data logging LED indicates data collection (solid at first and a slow blink after enough data has been collected for a fast static occupation, which is irrelevant for the base station). Make sure the data logging light is on before leaving your base station.
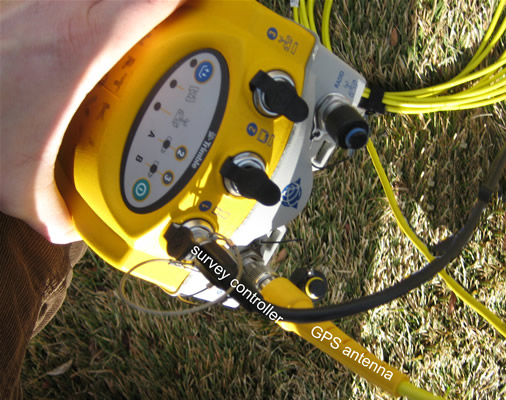
If you are using a survey controller to program your base, connect the survey controller to port 1 of the receiver as described in (3), above.
Turn on the survey controller by pushing the green power key. Power up the receiver by pushing the green power button if it is not already on. Double-click on the Survey Controller icon (TSCe, TSC2). The survey controller should recognize the GPS receiver; a receiver icon will appear on the screen, along with a GPS antenna with antenna height (the height will likely be wrong or show as a question mark) and a satellite icon with the number of satellites the receiver is tracking.
Select Survey in the lower left.
Select your chosen survey style (e.g. PP Kinematic or PPK).
Select "Start base receiver". You may have to re-enter some survey information, e.g. antenna type and logging device.
When the survey controller prompts you to remove the survey controller, remove the survey controller from the base receiver. Hit Okay.
Make sure the GPS receiver is fit to withstand any environmental dangers. Close the box, careful not to pinch any cables inside. Plug the pass-through with e.g. foam if heavy rains are expected.


Connecting and disconnecting lemo connectors to and from the GPS receiver.
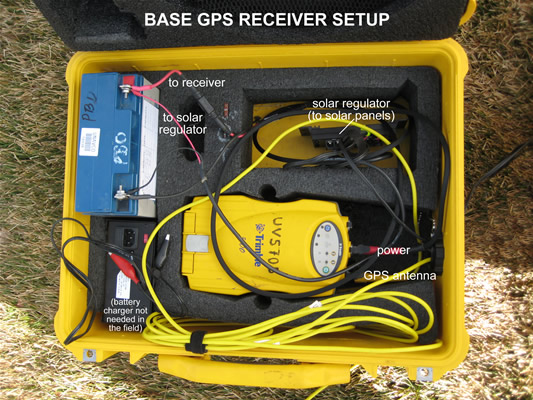
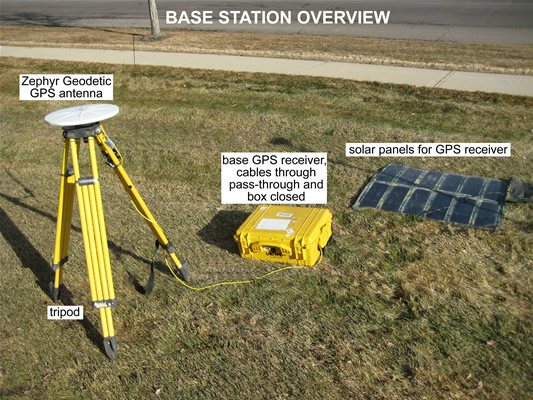


Base receiver and overall base station setup.
Setting up and running the rover
As with the base station, rover antenna setup may vary depending on the project goals. The suggested setup includes an antenna mounted on either a backpack mount (lower precision) or a range pole (higher precision).
Connect the GPS antenna to the antenna mount.
Connect the 90 degree end of the antenna cable to the antenna; uncoil just enough cable to reach from the antenna to the survey backpack with a small amount of slack. Place the rest of the cable, still coiled, inside the backpack. This will help to keep the cable tidy and unkinked. [If using a Trimble survey backpack, uncoil the appropriate amount of cable first and place the still-coiled cable in the backpack; pass the uncoiled end of the cable through one of the openings in the back of the backpack and connect the end to the antenna.]
If using internal batteries, put the internal batteries in the receiver and place the receiver in the backpack with the ports facing upwards. If using an external battery, put the battery in the survey backpack with the terminals protected and place the reciever on top of or beside it with the ports facing upwards. Connect the battery to the receiver using the battery cable and port 2 or 3 of the receiver.
Connect the straight end of the GPS antenna cable to the antenna port on the reciever.
Connect the survey controller cable to port 1 on the receiver using the survey controller cable. If using a Trimble survey backpack, pass the cable through one of the openings in the back of the backpack.
Turn on the survey controller and the receiver if they are not on already. As with the base, you should see reciever, antenna, and satellite icons on the controller’s screen. Select Survey in the lower left. Select your chosen survey style (e.g. PP Kinematic).
Select "Start survey". At the bottom of the screen, the controller will display survey messages. Possible messages are "Searching for satellites," "Poor PDOP," and "Initializing". If there is a positioning problem ("Searching for satellites," "Poor PDOP") move into a clearer area to increase the rover antenna’s sky view. As stated before, you must track at least 5 satellites in common with the base receiver. ’Initialization’ refers to collecting enough data (at least 8 minutes of continuous satellite tracking with 6 or more satellites) to be able to calculate high-precision solutions in the data processing. If ’lock’ or tracking of satellites is lost, you must reinitialize--that is, you must collect at least another 8 minutes or more of data without another interruption. You may start surveying points or mapping immediately upon starting the survey, but if you lose lock before initialization is gained, you may have low-precision (’Float’, as opposed to ’Fixed’) solutions. Be wary of ’Initialization lost’ messages.
To measure topo points:
Select Survey from the lower left of the main menu. Select "Measure Points".
Name the point and enter the antenna information. Select "Measure". DO NOT MOVE UNTIL POINT IS STORED. If you have set ’Auto store point’ to ’Yes’ in the survey configuration, your point survey will automatically stop after the required time. If you have set it to ’No,’ you will have to end the point survey by selecting "End".
Continue to measure points as needed.
Hit the Menu or Esc key/option to return to the main menu.
To measure points continuously (mapping):
Select Survey in the lower right of the main menu. Select "Continuous topo".
Enter antenna information. Select time interval. Points will be collected automatically based on this setting. Give a start point name; we highly recommend your point name ends in a number, as this last character will automatically be incremented in each point name.
Select "Measure" when ready.
Select "End" when done. Start and end point collection as much as needed.
Hit the Menu or Esc key/option to return to the main menu.
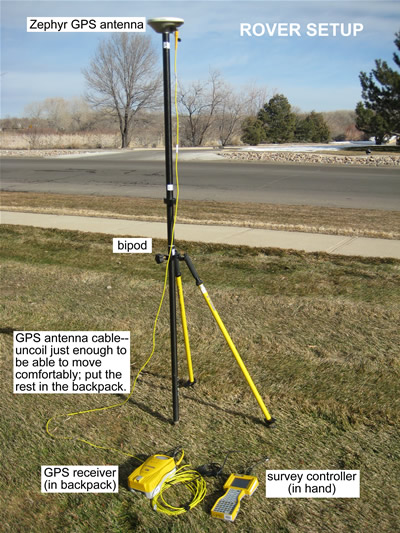


Rover setup.
Ending the survey at the rover
When you are done with your survey, press the Menu key to return to the main menu and select Survey from the lower left.
Select "End Survey". You can start and end a survey in the same job as many times as you like. When asked "Power down receiver?" select "Yes".
The message "Disconnect the cable from the controller" will appear. Disconnect the cable from the receiver and hit "OK".
Power down the survey controller by pressing and holding the green power key for 2 seconds. Do NOT continue to press the power button after the survey contoller begins powering down - this will force a hard reset.
If you have not already powered down the rover receiver, do so now by pressing and holding the green power button for 2 seconds. Do not continue to press the power button after the receiver has powered down.
Disassemble the rover equipment in any order. To disconnect cables from ports 1-3 on the receiver, pull the connectors straight out using the small metal cable attached to the connector. If there is no attached cable, grasp the upper part (closest to the cable, not the receiver) and pull. Do not force the connectors and NEVER TWIST the connectors, as the pins inside may break.
Return equipment to the original containers.
Ending the survey at the base
There is no need to reconnect the survey controller to the base station. Simply power down the receiver by removing the power cord if using external power, or by pressing and holding the power button for 2 seconds if using internal batteries (do not continue to press the power button after the receiver has powered down).
Remeasure the antenna height; check that the antenna is level and oriented to north. Note any problems with the antenna set-up.
Disassemble the base equipment in any order. To disconnect cables from ports 1-3 on the receiver, pull the connectors straight out using the small metal cable attached to the connector. If there is no attached cable, grasp the upper part (closest to the cable, not the receiver) and pull. Do not force the connectors and NEVER TWIST the connectors, as the pins inside may break.
Coil the cables carefully without kinking or twisting the cables. DO NOT coil the antenna cable around your arm, as this twists the cable.
Return equipment to the original containers.
Back in the Lab
Downloading Data
There are several options for downloading data from the GPS receiver and the survey controller.
Option 1 (preferred method): Direct download from the receiver or survey controller using the Trimble Data Transfer Utility
You will need the Trimble Data Transfer Utility. If you do not already have it loaded onto your computer, you can dowload it for free from the Trimble website (http://www.trimble.com/datatransfer.shtml) or the UNAVCO Knowledgebase (/questions/603/).
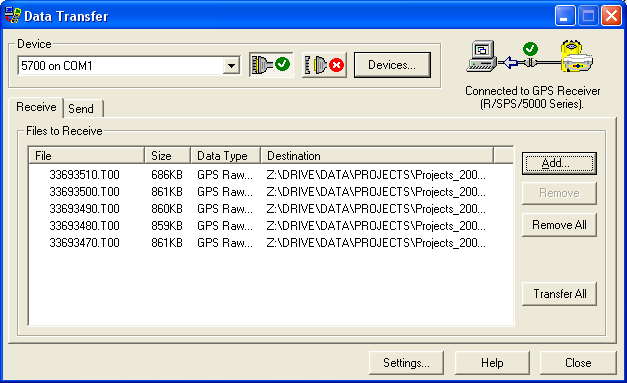
Screen shot of the Trimble Data Transfer Utility.
Connect the receiver or survey controller to a PC using the communications cable (4700, 5700, R7, TSC1) or a USB cable and dongle (TSCe). The communications cable is a serial cable; if using a laptop, you may need to use a serial-to-USB adapter. Power up the computer and the receiver or survey controller. If using a TSCe, the following message should appear: "Connect to desktop?" Select "Yes". A Microsoft ActiveSync window should appear on your computer screen, readying "Connected". If you do not have Microsoft ActiveSync, download it for free from Microsoft (http://www.microsoft.com/windowsmobile/en-us/help/synchronize/device-synch.mspx).
Open Trimble Data Transfer Utility.
If you do not connect automatically ("Connected to ..". message in the upper right), select the device from which you’d like to transfer data. If your device is not listed in the drop-down menu:
Click the "Devices" button.
Select "New" (lower left).
Select device from list, click "Okay".
Select the computer’s comm port that you are using, click "Next".
Enter a name for your device.
Set the serial port properties. Defaults should be fine; make sure "Data bits" = 8 and "Parity" = None. Click "Finish".
Click "Close" in the "Devices" window.
Your new device should now be added to the drop-down list.
Click the button with the green check mark.
Click "Add". In the "Open" window, browse for the folder you would like your data transfered into under "Destination".
Select the file(s) you would like transfered. Note that the file(s) will be named for the job(s) you created. Click "Open".
The selected file(s) should appear in the main Data Transfer Utility window. Click "Transfer All".
Close the Data Transfer Utility program and disconnet the survey controller.
The program will automatically convert .t01 and .t00 files to .dat files; both file types will be transfered to your computer, along with metadata (the ’job’ files).
Option 2: Download from the CF or PCMCIA card (5700, R7, TSC1)
This option is the easiest, but is not recommended for transfering any data that has been collected with the survey controller because of the potential for losing metadata (see Option 1). You may want to use this method for downloading data from your base receiver.
Insert the CF or PCMCIA (TSC1 only) into the appropriate card reader connected to a computer.
Select the files from the card that you wish to transfer; copy them to a directory on your computer.
On your computer, right-click on the file(s). Select "Convert to .DAT". A .dat file for each file selected will be created in the same directory. You must have the Trimble Data Transfer Utility on your computer to have access to this option.
Back up your data.
Data Processing
See "How to process fast-static and post-processing kinematic surveys using Trimble Geomatics Office" (/questions/613/).
bab2010
)